TPM in its most basic concept is a management philosophy that emphasizes the systematic elimination of losses and is carried out through technologies such as the 5 “S”, Manufacturing Cells, SMED, etc.
Based on customer needs, it aims to reorganize internal processes across the company's various areas to ensure the highest level of satisfaction for each of its stakeholders: customers, employees, the community, the environment, and shareholders.
Organizations that practice lean concepts make efficient use of their resources: technology, equipment, and especially the knowledge and skills of their staff. Lean enterprise management seeks to harness intelligence in every operation, from plant operators to senior management.
It is a comprehensive overview of how to manage a highly efficient organization, beyond manufacturing areas, since the "lean" concept applies to all business processes.
He TPMAs a privileged tool for creating a Lean Enterprise, TPM is a management methodology aimed at optimizing business assets through the total elimination of losses. By identifying these losses in the production process and transforming them into opportunities for improvement, TPM will promote cost reduction and ensure greater competitiveness.
The methodology of the TPM It teaches how to analyze the gaps between the ideal condition and the actual situation in all of the organization's assets so that it is possible to measure the gap and establish recovery goals, which will ensure greater capacity for the production process with minimal investment.
For more than 30 years the TPM It has been showing that in every company, there is another company of equal size and capacity that isn't producing, that is hidden behind problems and organizational losses. TPM is the best tool to bring to light what's latent in your organization and put it to work for your benefit.
He TPM It is a Comprehensive Management System that, starting from the productive areas, seeks to identify and eliminate losses throughout the company.
To do this, it manages the entire company through an organizational structure, whose main orientation is a Creative Approach to Losses, through the activities of the Small Overlapping Autonomous Groups and gradually involving All Departments (Engineering, Sales, Administration, Finance, Planning), already ALL Staff, from senior management to plant operators, in one project: ZERO LOSSES.
How is it implemented?
It is a philosophy of systematically combating losses that includes working with the following tools:
- 5 “S” (Strategies for Effective Businesses)
- Standardization and Visual Control
- Poka Yoke
- Kaizen Teian (Total Staff Involvement Program)
- Cellular Manufacturing (Work Cells)
- OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
- SMED (Rapid Tool Preparation)
- JIT (Just In Time)
- Muri Mura Muda (Three Great Losses)
- Systematic elimination of activities that do not add perceived value to the customer.
- Situational Leadership
What is TPM?
It is a Prevention Technology that achieves:
- Early detection of irregularities.
- Take corrective measures.
- Prevent deterioration.
- Increase the quality of inspections.
- Administration of causes (inspection and early verification of causes), not consequences.
- Always in search of “Zero,” ensuring that the phenomenon we are preventing does not appear.
- Maintain the basic state of the equipment.
What does TPM entail?
Maximize production with everyone's participation:
- Train operators to be able to detect defects, perform inspections, lubricate, and replace parts.
- Create pleasant work areas and easy-to-operate machines with high productivity.
- Keep the facilities in perfect condition.
Keeping machines in optimal condition:
- They work so well that they never break down.
- They operate at the design speed. Or faster.
- They operate without downtime or minor stops.
- They never make defective products.
- They cause minimal losses during start-ups, assembly and adjustments.
- Operators work safely and comfortably.
- Establish and maintain standardized methods for:
- Equipment diagnosis.
- Early detection of abnormalities.
- Spare parts management.
- Computer systems that maintain a history of equipment and fault data.
The methodology, as implemented by Action Group, remains faithful to the basic principles established by the Japanese Institute of Plant Maintenance, but has been adapted to the local culture. To achieve this, we have taken the best of OD (Organizational Development) and TPM to create a unique methodology with a high impact on results.
Through its implementation in all types of industries and with a clear focus on business losses, it transforms organizational culture and drastically reduces costs, making the concept of a lean enterprise a reality.
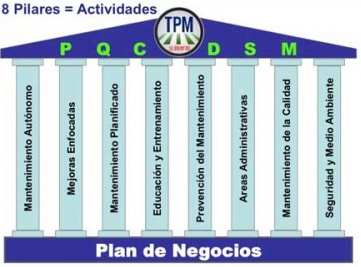
See: The Pillars of TPM (An Implementation Strategy)
See: What is TPM and what is it for? By Raúl A. Perez Verzini